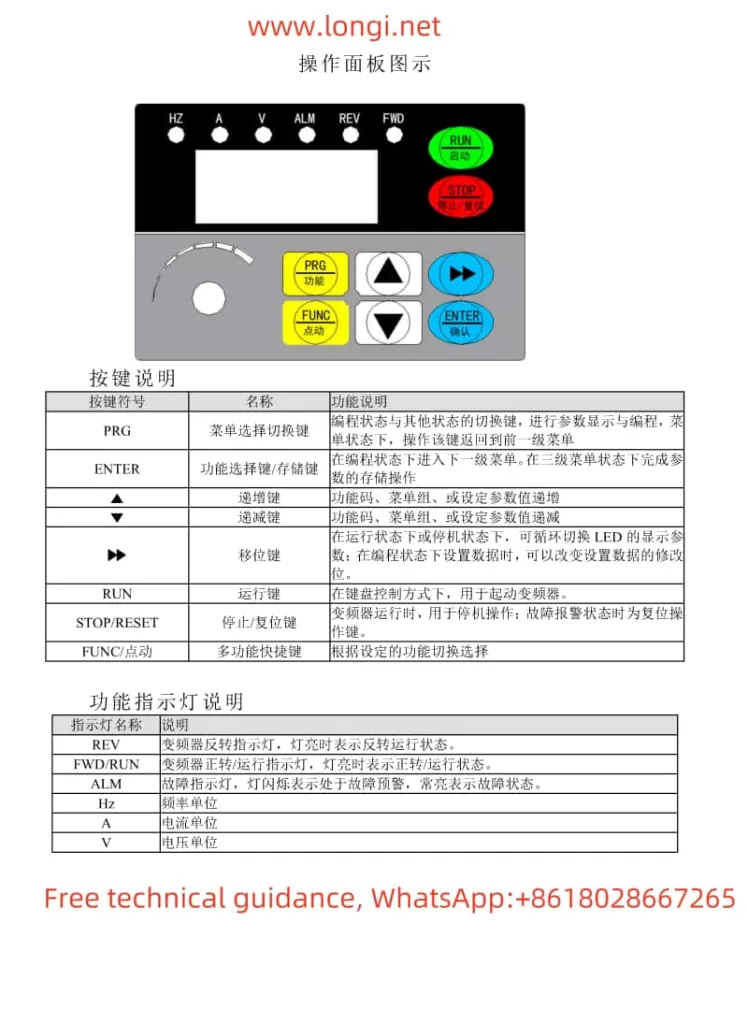
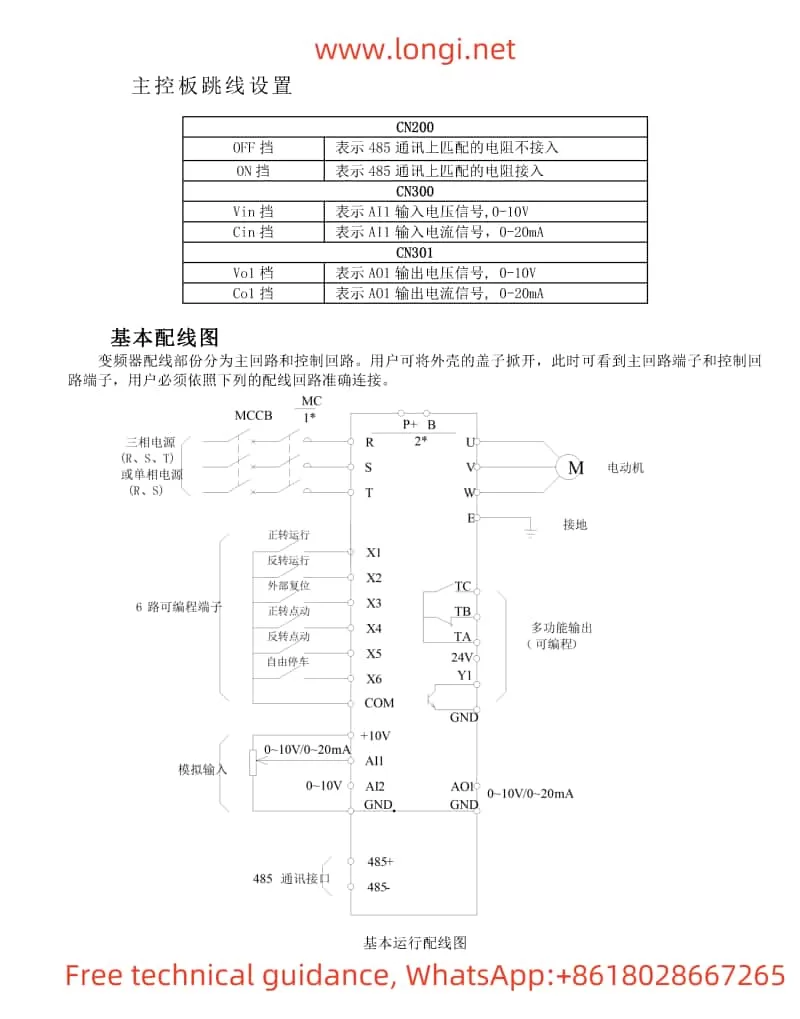
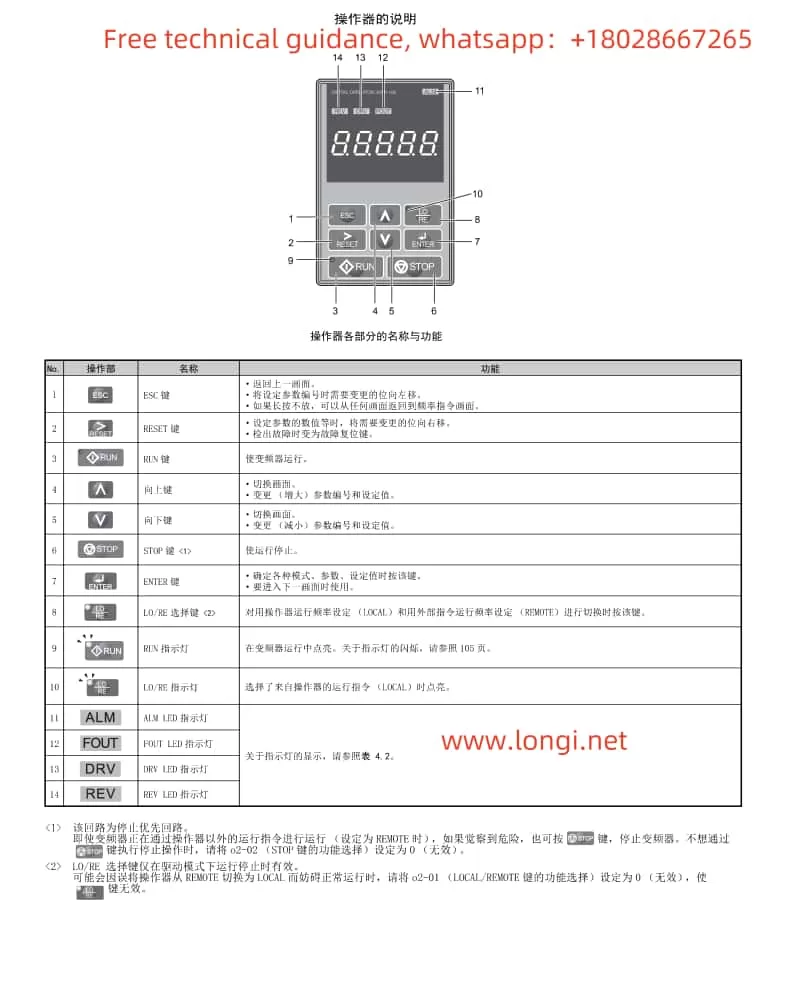
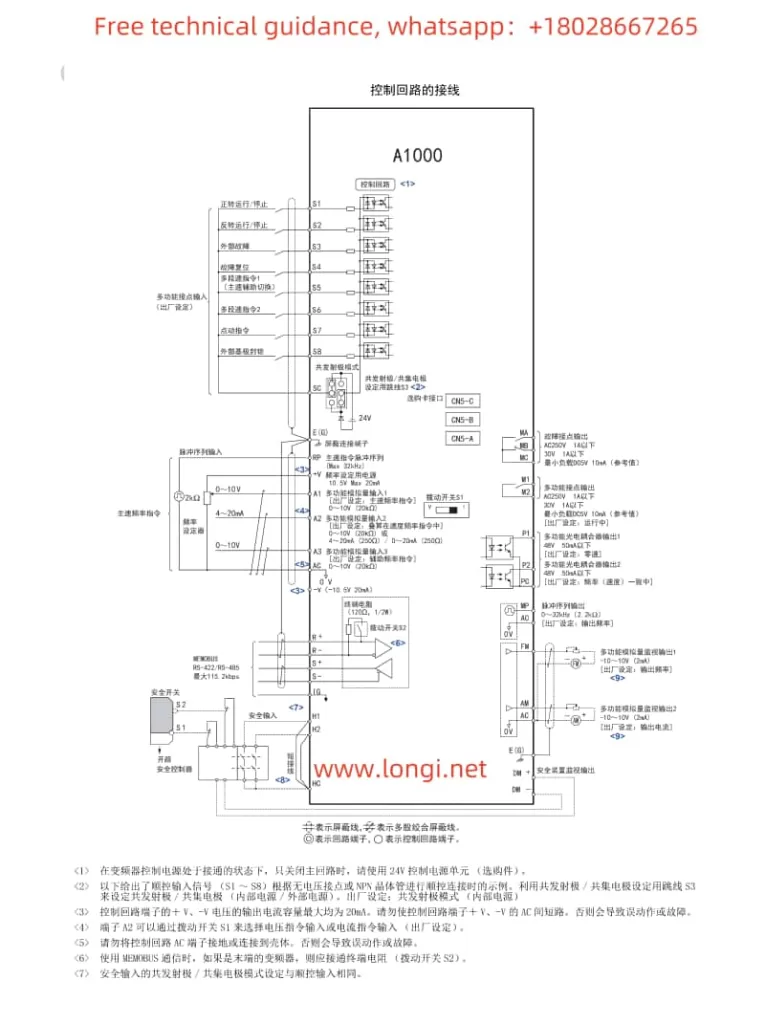
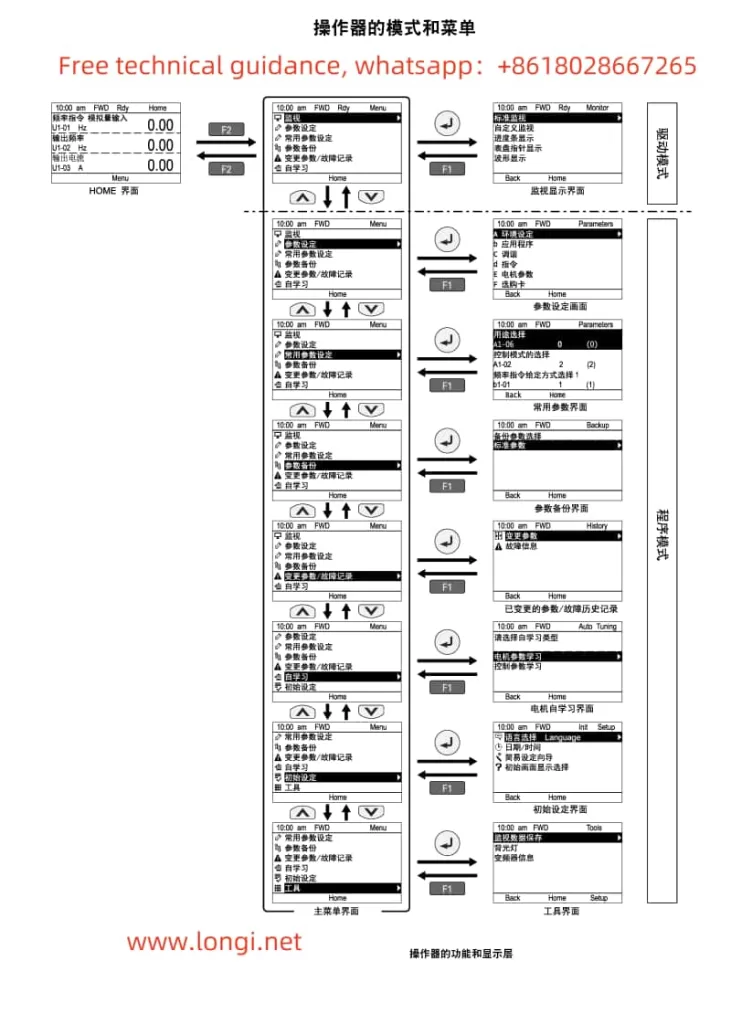
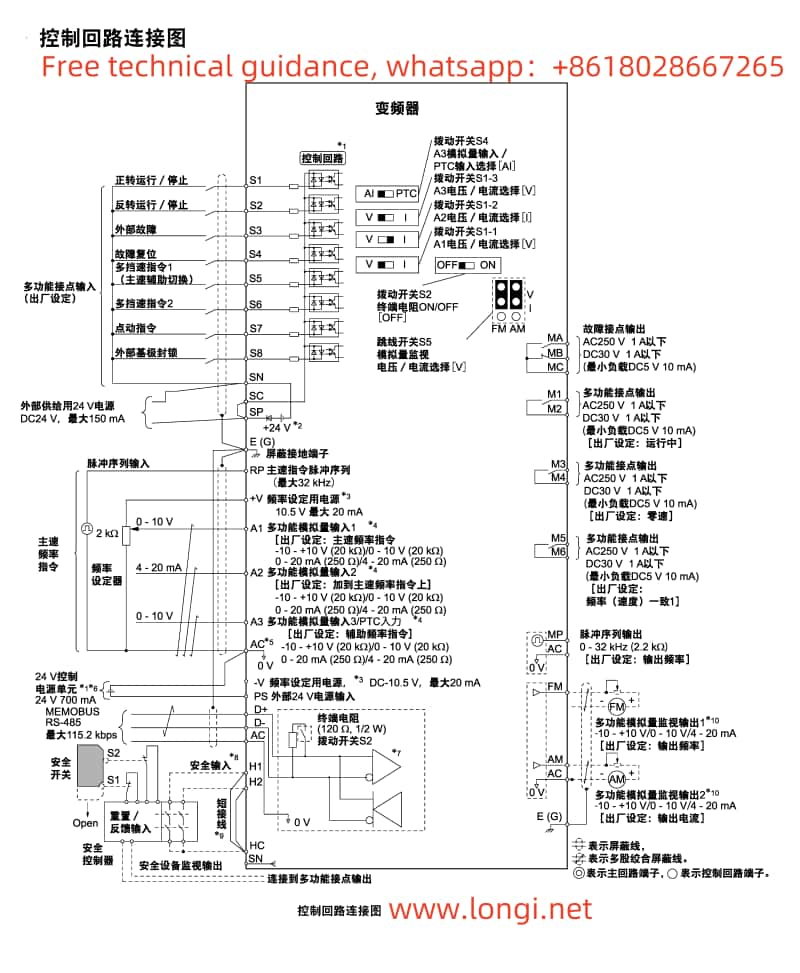
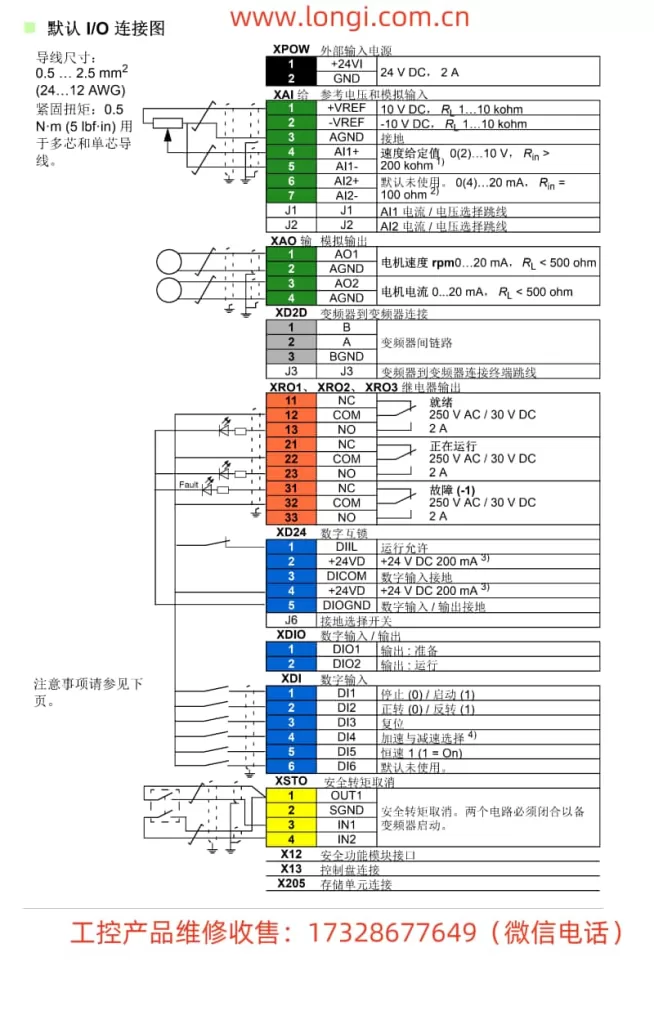
I. Operation Panel Function Description and Basic Operations
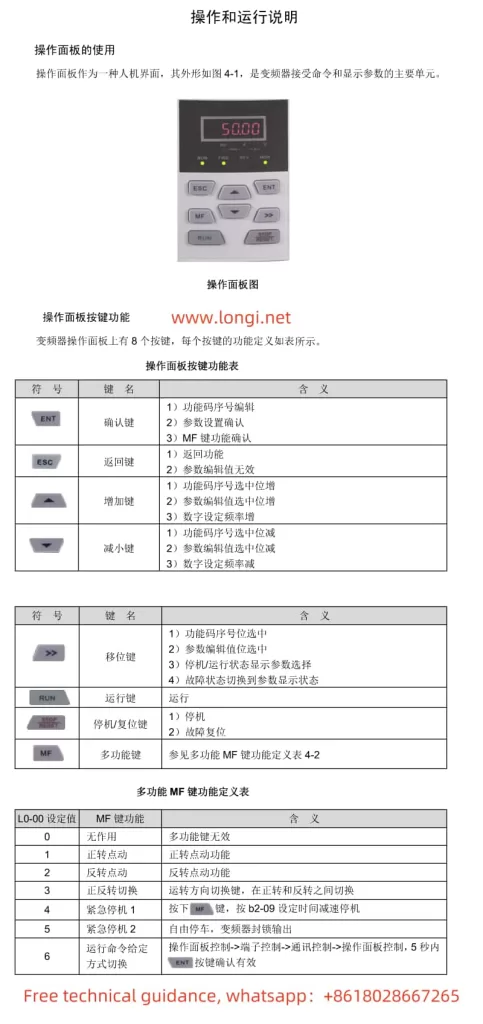
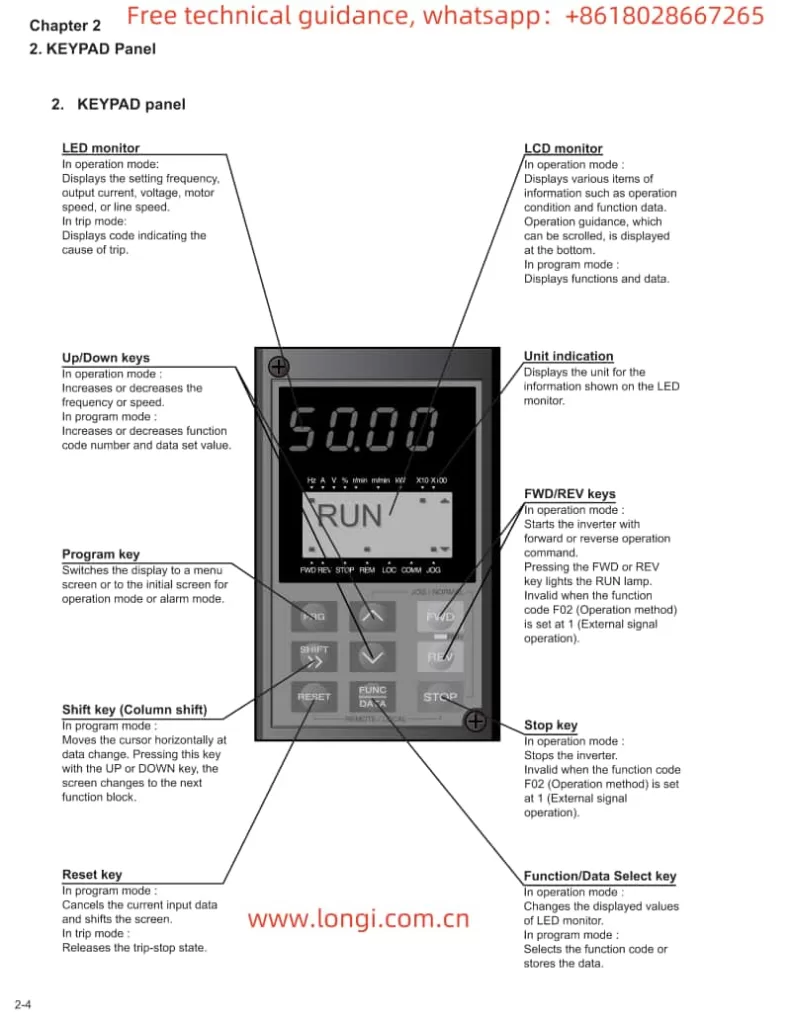
Operation Panel Functionality
The Inovance CS700 series crane-specific inverter is equipped with an intuitive and user-friendly operation panel, which primarily includes the following buttons and indicators:
- Buttons: Including PRG (programming key), ENTER (confirmation key), increment key (▲), decrement key (▼), shift key (◀/▶), RUN (run key), STOP/RES (stop/reset key), MF.K (multi-function key), QUICK (menu key), etc.
- Indicators: Including RUN (run indicator), LOCAL/REMOT (command source indicator), FWD/REV (forward/reverse indicator), TUNE/TC (tuning/torque control/fault indicator), etc.
Basic Operations
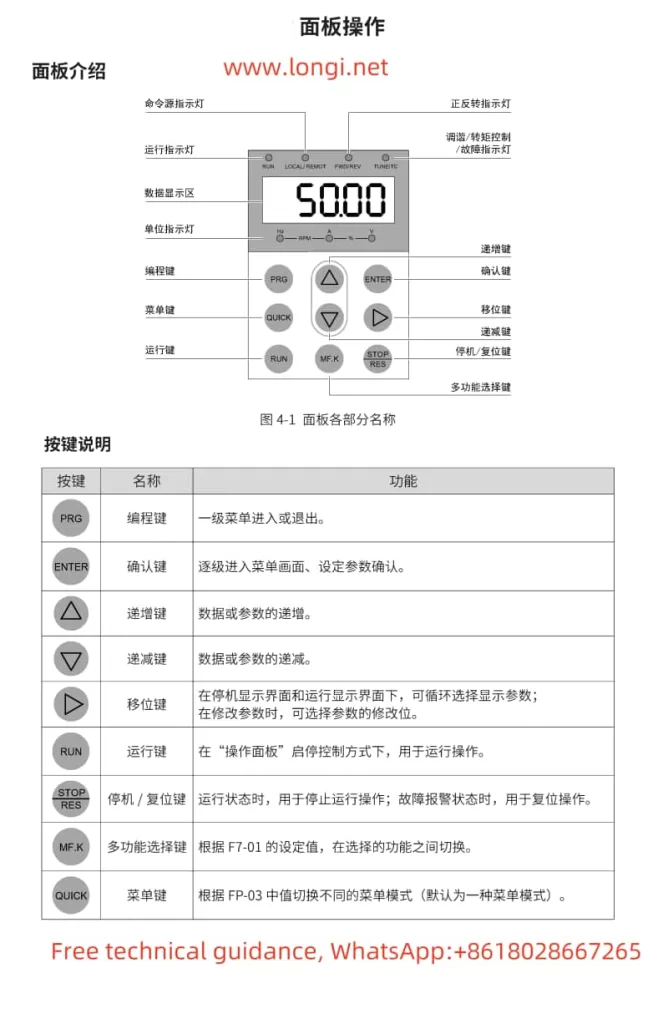
- Start and Stop:
- Press the RUN button to start the inverter, and the inverter run indicator (RUN) will light up.
- Press the STOP/RES button to stop the inverter, and the inverter run indicator will go out.
- Speed Regulation:
- Enter the programming mode by pressing the PRG button, adjust the target frequency using the increment key (▲) and decrement key (▼), and then press the ENTER button to confirm.
Password Setting and Removal
- Password Setting: Set the password for all function parameters through parameter AF.00, the password for the second-level menu through parameter bF.00, and the password for the third-level menu through parameter FF.00.
- Password Removal: Set the password parameter to 0 to remove the password protection.
Parameter Initialization
- Press the PRG button to enter the programming mode, select parameter AF.01 (restore factory parameters for the first-level menu), bF.01 (restore factory parameters for the second-level menu), or FF.10 (restore factory parameters for the third-level menu), and press the ENTER button to confirm.
II. Crane Mode and PG Encoder Feedback Settings
Crane Mode Selection
The CS700 series inverter supports multiple crane modes, generally achieved through the multi-speed function. The specific setting steps are as follows:
- Enter the programming mode, select parameter A0.07, and set it to 0 to choose multi-speed as the frequency source.
- Set parameters b3.01~b3.05 to define DI1~DI5 as multi-speed selections 1~5, respectively.
- Set the corresponding frequency for each speed in parameters b5.00~b5.07.
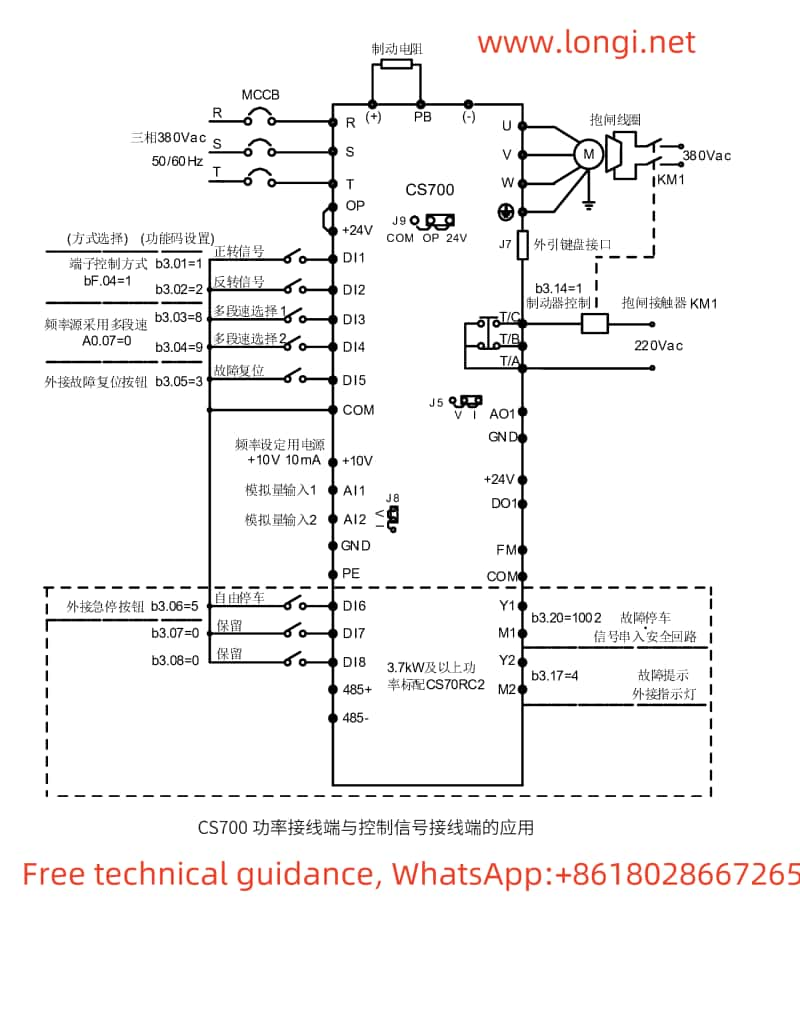
PG Encoder Feedback Settings
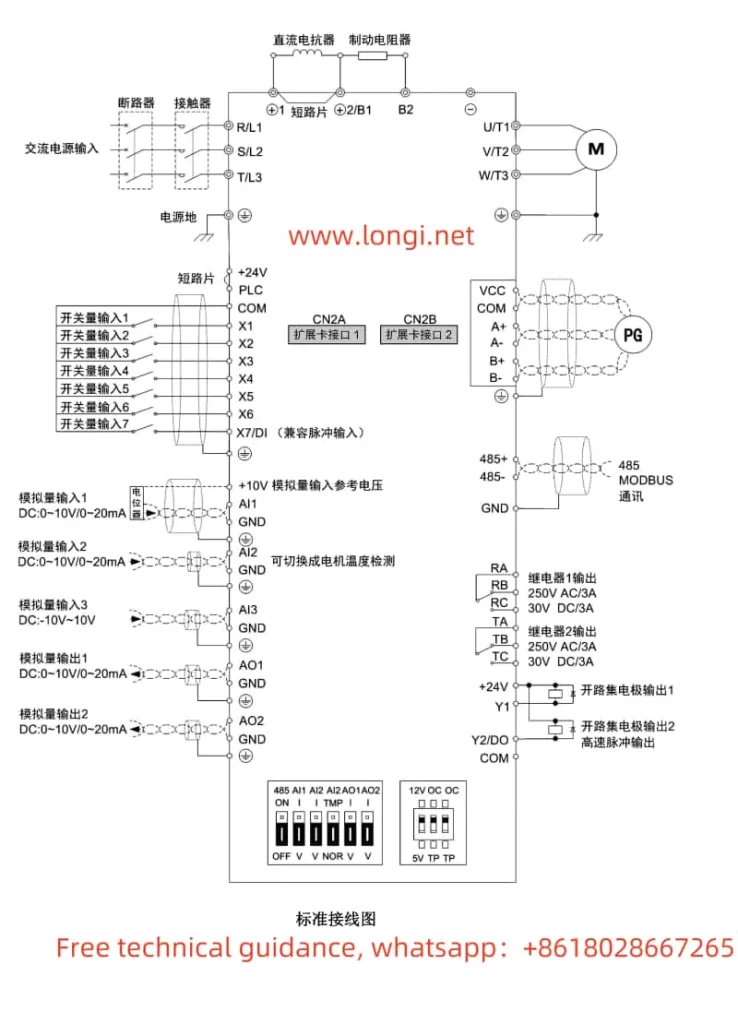
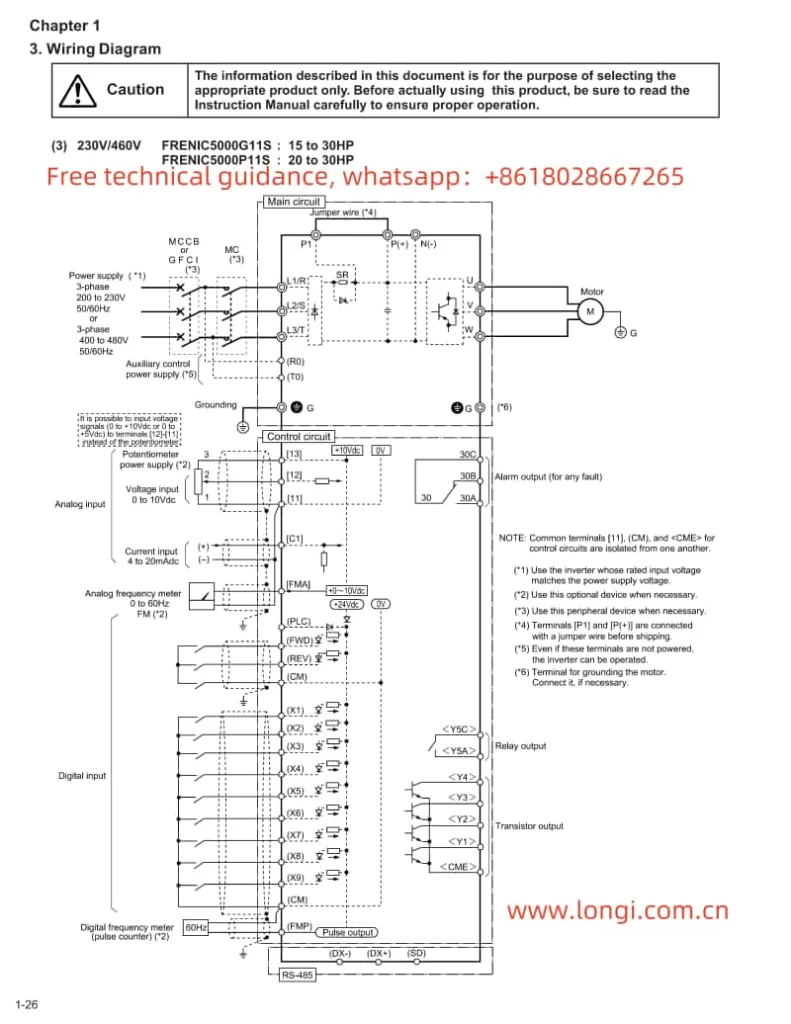
If PG encoder feedback is selected, the following settings and wiring are required:
- Parameter Settings:
- Enter the programming mode, select parameter b1.00, and set it to 1 to choose encoder vector control (closed-loop control mode).
- Set parameters b2.00 (encoder lines) and b2.01 (encoder type) according to the actual encoder type used.
- Wiring:
- Connect the encoder signal wires to the PG card interface of the inverter, with specific wiring reference to the wiring diagram in the manual.
III. Fault Code Meanings and Solutions
The CS700 series inverter provides a wealth of fault codes to help users quickly locate and resolve issues. Below are some common fault codes, their meanings, and solutions:
- Er02: Acceleration Overcurrent
- Meaning: Grounding or short circuit in the inverter output circuit, or too short acceleration time, etc.
- Solution: Check the peripheral circuit and eliminate grounding or short circuit faults; increase the acceleration time.
- Er03: Deceleration Overcurrent
- Meaning: Grounding or short circuit in the inverter output circuit, or too short deceleration time, etc.
- Solution: Check the peripheral circuit and eliminate grounding or short circuit faults; increase the deceleration time.
- Er04: Constant Speed Overcurrent
- Meaning: Grounding or short circuit in the inverter output circuit, or low voltage, etc.
- Solution: Check the peripheral circuit and eliminate grounding or short circuit faults; adjust the voltage to the normal range.
- Er05: Acceleration Overvoltage
- Meaning: High input voltage, or external force dragging the motor during acceleration, etc.
- Solution: Adjust the voltage to the normal range; eliminate external force dragging or install braking resistors.
- Er08: Control Power Supply Fault
- Meaning: Input voltage is not within the specified range.
- Solution: Adjust the voltage to meet the specified requirements.
- Er10: Inverter Overload
- Meaning: Excessive load or motor stall, or undersized inverter selection, etc.
- Solution: Reduce the load and check the motor and machinery; select an inverter with a larger power rating.
- Er11: Motor Overload
- Meaning: Improper setting of motor protection parameters, or excessive load, etc.
- Solution: Set the motor protection parameters correctly; reduce the load.
- Er12: Input Phase Loss
- Meaning: Abnormal three-phase input power.
- Solution: Check and eliminate issues in the peripheral circuitry.
- Er14: Module Overheat
- Meaning: High ambient temperature or blocked air duct, etc.
- Solution: Lower the ambient temperature and clean the air duct.
- Er37: Frequency Direction Anomaly
- Meaning: The direction of the given running frequency is opposite to that of the motor feedback frequency.
- Solution: Check the motor parameter settings and adjust parameter bC.02 if necessary.
- Er41: Loose Brake Fault
- Meaning: Error in the input of the loose brake feedback signal.
- Solution: Check the brake circuit wiring and the function selection of the control panel’s loose brake feedback input point.
- Er42: Holding Brake Fault
- Meaning: Error in the input of the holding brake feedback signal.
- Solution: Check the brake circuit wiring and the function selection of the control panel’s holding brake feedback input point.
IV. Conclusion
The Inovance CS700 series crane-specific inverter is a powerful and easy-to-operate inverter dedicated to crane equipment. Through this guide, users can quickly master the basic functions of the operation panel, the setting method for crane modes, the configuration steps for PG encoder feedback, and solutions to common fault codes. It is hoped that this user guide will help users better use and maintain the CS700 series inverters, improving the work efficiency and safety of crane equipment.