Introduction
The Fuji FRENIC 4600 series high-voltage inverters are widely used in industrial drive systems, playing a vital role in driving large power equipment due to their stable performance and efficient control capabilities. However, after long-term use or idle periods, inverters may experience some faults, particularly in cases of electrical connection issues or abnormal motor loads. Common faults include PWM fiber optic connection errors and motor overload alarms. These faults are often interrelated, and it is necessary to perform a thorough analysis to determine the root cause of the failures and take corrective actions.
This article will analyze the relationship between PWM fiber optic connection errors and motor overload faults, explore the fundamental causes behind these issues, and propose targeted solutions based on systematic troubleshooting methods.
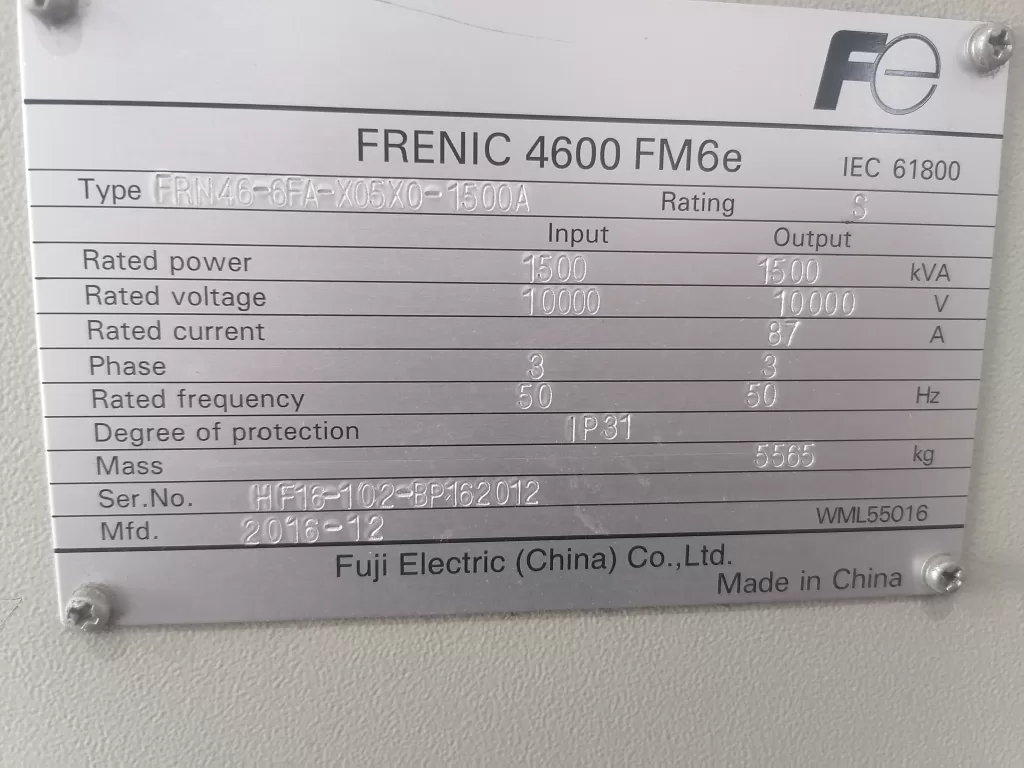
1. Causes and Analysis of PWM Fiber Optic Connection Errors
1.1 Fiber Optic Connection Issues
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) fiber optic connections are a critical path for signal transmission between the inverter’s internal control system and external devices. When there is instability or loss of the fiber optic connection, the inverter may fail to receive or transmit control signals correctly. Common fiber optic connection issues include:
- Loose or Damaged Fiber Optic Connectors: Over time, after prolonged use or idle periods, the fiber optic connectors may become loose, oxidized, or physically damaged, resulting in unstable signal transmission.
- Pollution or Obstruction of Fiber Optic Connectors: Dust, oil, and other substances can accumulate on fiber optic connectors, impacting the quality of signal transmission, which may lead to connection errors.
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): In environments with strong electromagnetic interference, signals can be disrupted, causing errors in fiber optic communication.
When these issues occur, the inverter’s signal transmission is interrupted or distorted, preventing the control system from regulating the motor’s operation properly.
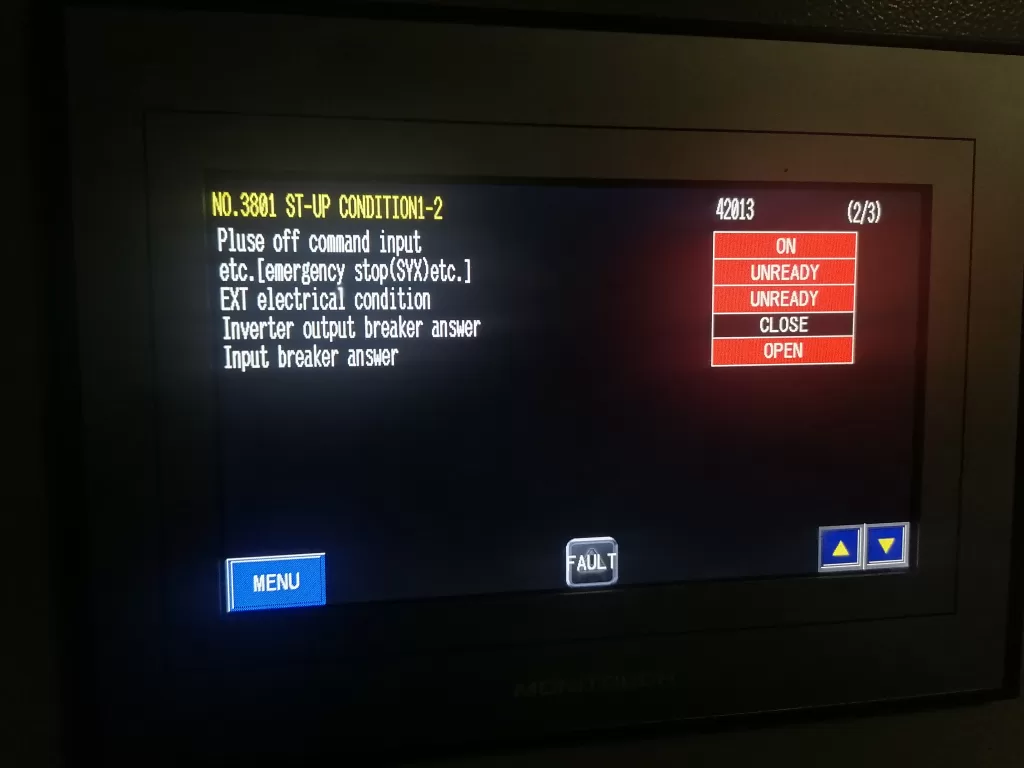
1.2 Triggering Mechanism of Motor Overload
When a fiber optic connection error occurs, the inverter may fail to obtain accurate motor status information or adjust the output frequency correctly. Without proper regulation of the motor load and operating conditions, the inverter may generate unstable power or current output, resulting in motor overload.
- Loss of Control Signals: With a fiber optic connection error, the inverter cannot receive feedback from the motor, leading to an inability to regulate the motor’s load properly, which causes excessive current and triggers the overload alarm.
- Frequency Regulation Failure: If the inverter cannot correctly adjust the output frequency due to fiber optic signal loss, the motor may run at non-optimal settings for extended periods, leading to overload.
- Excessive Inrush Current During Startup: Without proper communication through fiber optic signals, the inverter may fail to handle the large inrush current during motor startup, resulting in an overload fault.
2. Correlation Between Fiber Optic Connection Errors and Motor Overload
From the fault diagnosis experience, PWM fiber optic connection errors and motor overload are closely related. Fiber optic connection errors typically serve as the root cause, while motor overload is a direct consequence of this issue.
- Protection Mechanism Triggered by Signal Loss: If the inverter cannot obtain motor feedback due to a fiber optic connection issue, the system may enter a “protection mode” and activate overload protection. This prevents the system from operating normally, resulting in excessive current flowing through the motor and triggering an overload alarm.
- Incorrect Motor Load Detection: Without proper fiber optic feedback, the inverter may misinterpret the motor load, causing the system to falsely detect an overload condition and activate the protection mechanism unnecessarily.
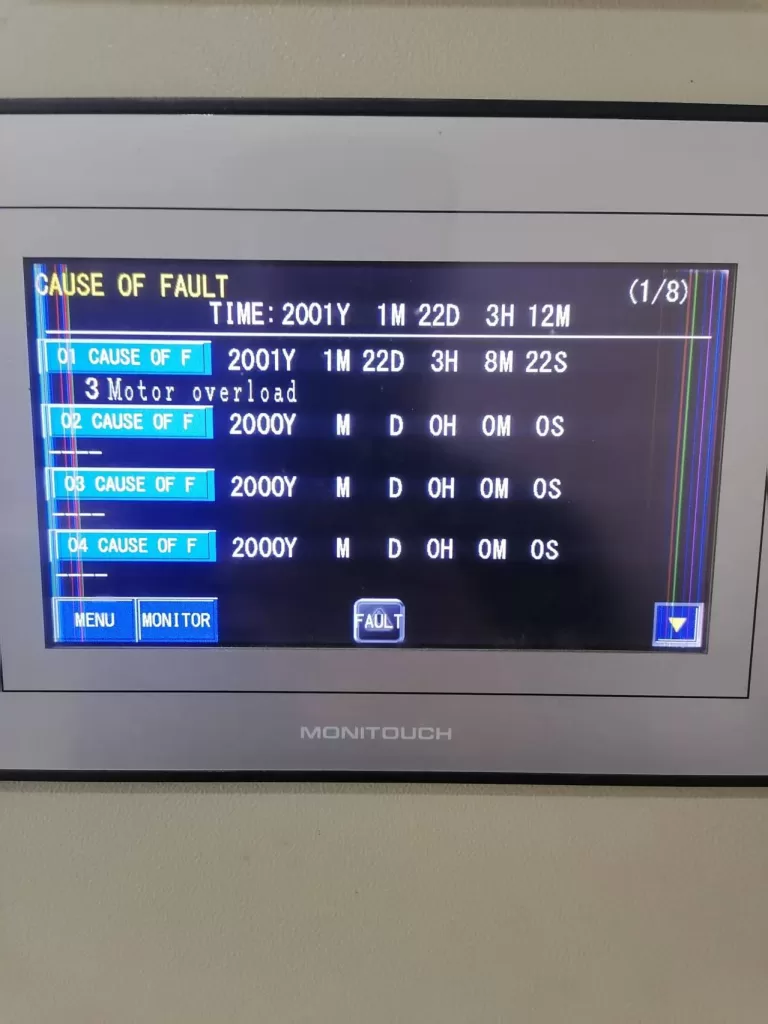
3. Fault Analysis and Troubleshooting Steps
3.1 Power Off and Reset
Since a fiber optic connection issue can trigger the inverter’s internal protection mechanism, the first step is to perform a power off and reset operation. Disconnect the power, ensuring the system is completely powered off, then execute the inverter’s reset procedure to clear all alarm information.
3.2 Inspect Fiber Optic Connections
After the reset, the next step is to inspect the PWM fiber optic connections for any issues such as looseness, damage, or contamination. Prolonged use or idle periods may cause degradation in fiber optic connectors. Follow these steps to check the fiber optic connections:
- Check the Connectors and Cables: Ensure that the fiber optic connectors are secure, free from oxidation, and that the cables are not damaged or broken.
- Clean the Fiber Optic Connectors: Use cleaning tools to remove any dust or oil contaminants from the fiber optic connectors to ensure proper signal transmission.
- Replace Fiber Optic Cables: If the fiber optic cables are damaged, they should be replaced immediately.
3.3 Inspect the Motor and Load
Once the fiber optic connection issue is resolved, inspect the motor and load for potential faults. Motor overload may also be caused by mechanical issues with the motor or abnormal load conditions. Check the motor’s condition and verify that the load is within normal operating limits:
- Check the Motor Condition: Use a multimeter to test the motor’s winding resistance to ensure there are no short circuits or grounding faults.
- Check the Load Equipment: Ensure that the load connected to the motor is not too heavy or jammed. Examine the mechanical components for signs of resistance or abnormal wear.
3.4 Check Inverter Control Parameters
If no issues are found with the motor or load, the next step is to check the inverter’s control parameters. Ensure that the overload protection and current limit settings on the inverter are correct and aligned with the motor’s rated specifications:
- Adjust Overload Protection Settings: Modify the inverter’s overload protection parameters according to the motor’s rated power and load requirements to avoid overly sensitive triggering of the protection mechanism.
- Set Frequency Limits: Verify that the inverter’s frequency settings are within the motor’s maximum operating frequency range to prevent overload conditions caused by excessive frequency.
3.5 Inspect Current Detection Circuit
Finally, check the inverter’s current detection circuit for functionality. A faulty current sensor or circuit could lead to incorrect readings, resulting in false overload alarms. Use the inverter’s diagnostic functions to inspect the current sensor and replace or repair it as needed.
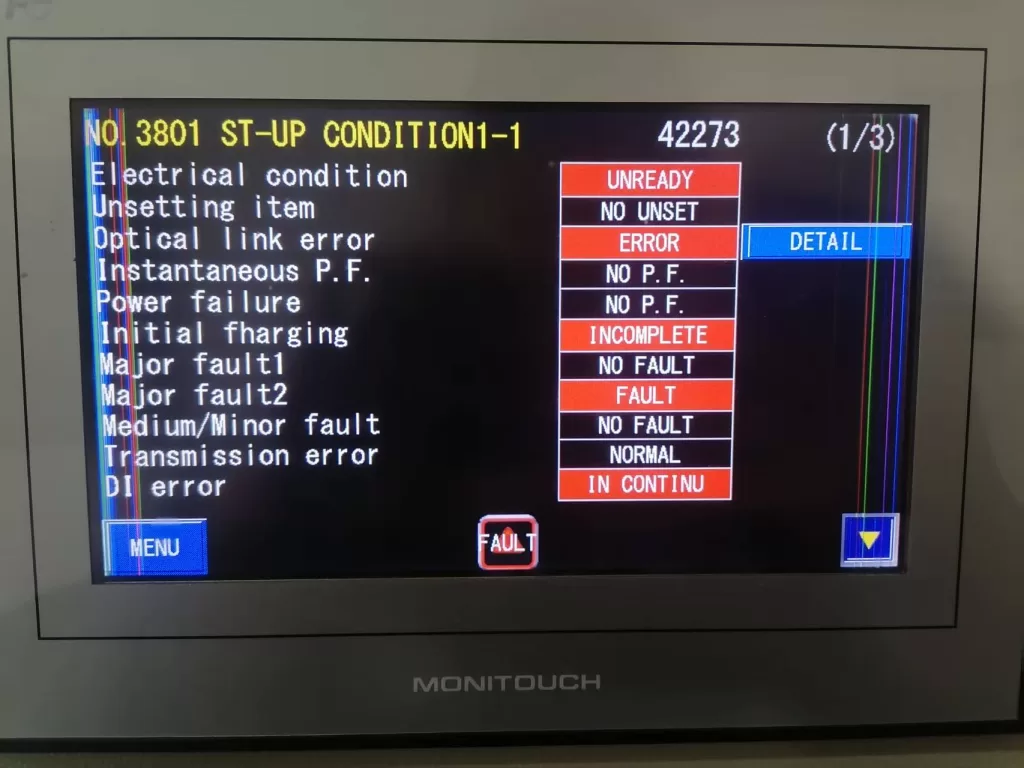
4. Conclusion
The PWM fiber optic connection error and motor overload fault in the Fuji FRENIC 4600 series inverter are often interrelated, with the fiber optic connection issue serving as the root cause and the motor overload being a direct consequence. Fiber optic connection errors result in signal loss, which prevents the inverter from properly regulating the motor load and frequency, triggering an overload alarm. By systematically checking fiber optic connections, motor conditions, inverter parameters, and current detection circuits, these faults can be resolved, and the system can return to normal operation. Throughout the troubleshooting process, it is essential to prioritize high-voltage safety and follow proper electrical safety protocols to ensure the safety of both the equipment and personnel.
