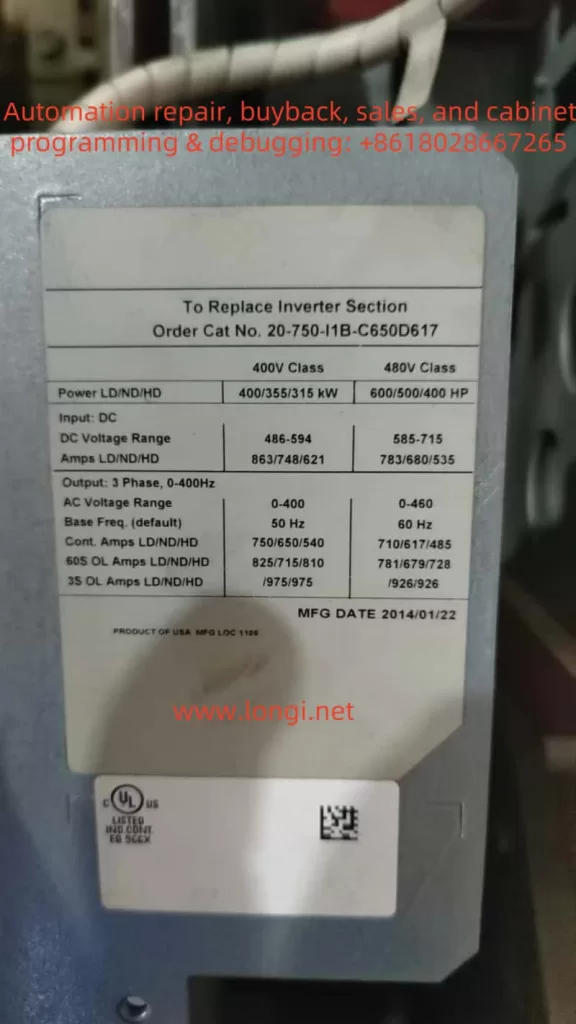
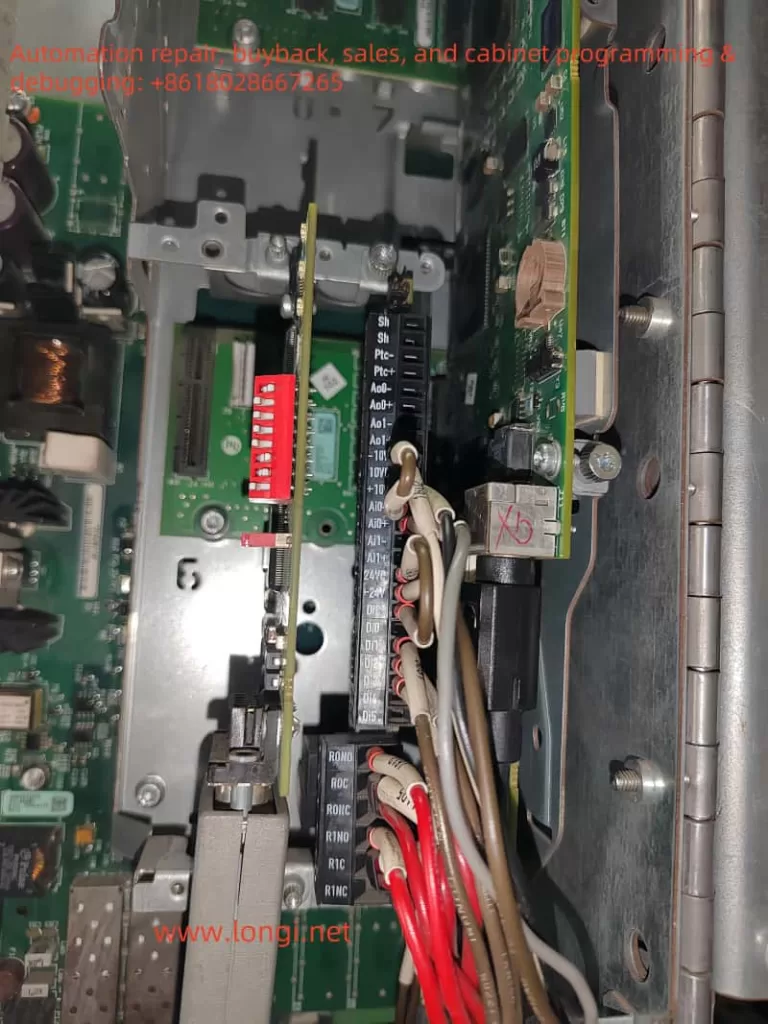
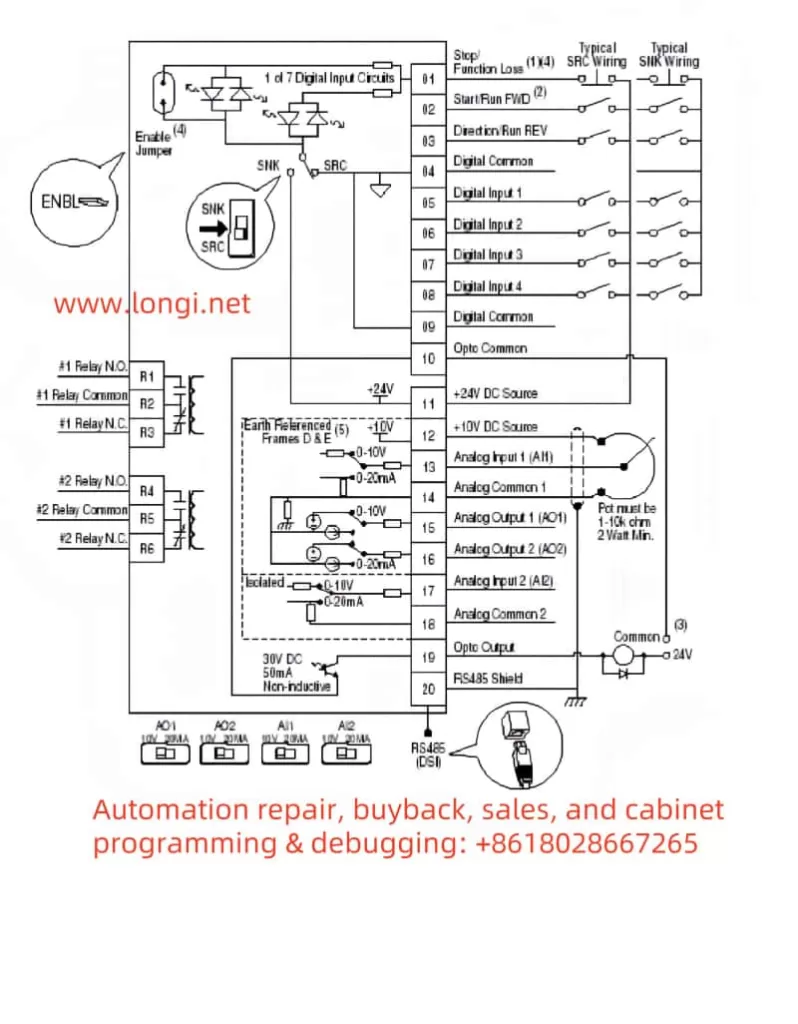
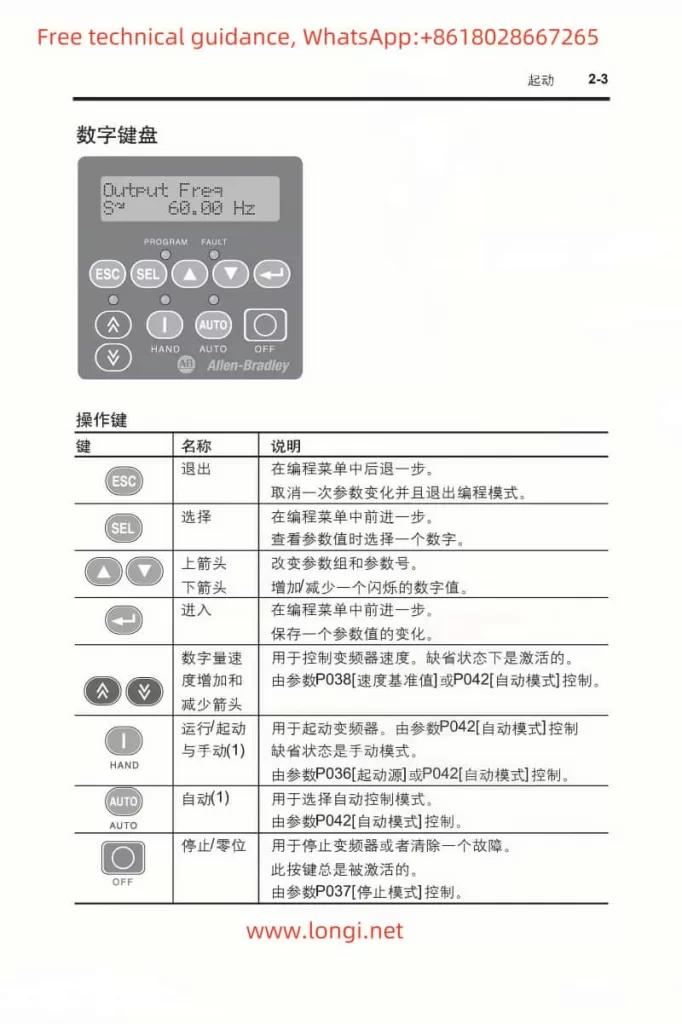
In modern industrial automation, variable frequency drives (VFDs) play a crucial role in adjusting motor speed, achieving energy savings, and providing precise control. Rockwell Automation’s PowerFlex 400 series, designed specifically for fan and pump applications, is known for its rich functionality and high stability. However, even the best drives can still encounter fault alarms in complex industrial settings. This article focuses on FAULT 017 (“Input Phase Loss”), commonly seen on the PowerFlex 400 series, offering an in-depth look at its implications and a clear, actionable approach to troubleshooting and remediation. With over a thousand words, it aims to provide practical, original guidance for readers.
I. Brief Overview of the Fault
Among the numerous fault codes of the PowerFlex 400, FAULT 017 (Input Phase Loss) often signifies a detected imbalance or loss of phase in the drive’s three-phase input power supply. In essence, the drive will trigger this alarm if one of the three-phase voltages is missing, or if the voltage imbalance exceeds the permissible threshold. Once triggered, the drive will shut down output to protect the power module—i.e., the rectifier, DC bus, and inverter section—from further damage.
From an application standpoint, fans and pumps commonly present large rotational inertia and high startup currents. If system voltage fluctuations are not well controlled, or if the power grid experiences significant swings, the drive is more likely to perceive an “input phase loss.” Furthermore, many users install fuses or circuit breakers upstream to protect the drive; a single blown fuse or faulty breaker contact in one phase can also cause this fault. Thus, FAULT 017 is not an isolated problem but rather a comprehensive alarm related to external power supply quality, the operational state of the load, and the health of the drive itself.

II. Causes and Underlying Principles
- Line-Side Phase Loss or Severe Voltage Drop
- In a three-phase circuit, if one fuse is blown, a circuit breaker trips on a single phase, or if a connection terminal is badly loosened, the drive might only receive two phases (or even one phase). Consequently, the rectifier section cannot create a balanced DC bus voltage, triggering the phase-loss alarm.
- Large, sudden dips in voltage (caused by unexpected loading, inadequate transformer capacity, etc.) can also be interpreted by the drive as “lost input phase.”
- Incorrect Fuse or Circuit Breaker Rating
- If the chosen fuse/circuit breaker is undersized, or not matched to the nameplate specifications of the drive, the high inrush current when starting may cause one fuse to blow. Alternatively, continuous operation near or above rated limits can blow fuses in a single phase, leading to a phase loss alarm.
- Defective Contactors or Loose Input Terminals
- In industrial settings, loose terminal screws, oxidation, and contactor burn marks are quite common. These can cause abnormal current flow in one phase, resulting in voltage imbalance and triggering the alarm.
- Malfunction of the Drive’s Internal Rectifier or Detection Circuit
- Damage to the drive’s internal rectifier bridge, DC bus, or current detection modules—whether caused by overvoltage spikes or component aging—can lead the drive to incorrectly (or correctly) identify a phase loss. If external measurement confirms normal supply voltage, yet the fault persists, internal hardware failure is likely.
III. On-Site Troubleshooting Approach
- Safe Shutdown and Visual Inspection
- Always power off the system and wait at least three minutes before any inspection, giving sufficient time for internal high-voltage capacitors to discharge and ensuring safety. Check the drive’s cooling channels, enclosure, and cable terminals for signs of burn, overheating, or odor. If abnormalities are observed, the drive casing may need to be opened for a deeper inspection of internal components.
- Measuring Three-Phase Input Voltage
- Use a multimeter or clamp meter to measure voltages at R/L1, S/L2, T/L3 and check whether they are in the correct phase-to-phase range (normally ±10% of the drive rating). If one phase has no voltage or is significantly lower than the other two, focus on that line’s fuse, circuit breaker, or input terminal first.
- Fuse and Circuit Breaker Checks
- Reference the standard fuse or breaker sizing recommended in the drive manual to ensure proper matching. If a fuse is found to be blown or a breaker has tripped on one phase, replace it and investigate the cause (overload or short circuit).
- Confirm the breaker has not partially tripped, leaving only two phases powered.
- Inspection of Contactors and Terminal Tightness
- In systems with contactor switching or star-delta transition, worn or pitted contacts can cause open-phase conditions. Examine all contacts with a meter to ensure they behave consistently.
- Tighten all terminal screws on the drive input; vibration or temperature changes can loosen them over time.
- Re-energize and Reset Fault
- After external electrical issues are remedied, reapply power to the drive and see if the fault resets automatically or if a manual reset is required (consult the drive’s manual in Chapter 4, “Fault Handling”). If the fault remains, the drive may have an internal hardware failure.

IV. Root Cause Analysis and Countermeasures
- Poor Power Supply Quality
- Some plants have large loads starting or stopping simultaneously, causing dramatic voltage dips or fluctuations. Consider adding a line reactor or isolation transformer ahead of the drive to buffer against such interference. Where possible, upgrading network capacity or reducing high inrush loads can also mitigate phase-loss alarms.
- Aging Components or Improper Ratings
- If slow-blow fuses are unsuited for the motor startup characteristics, or if circuit breakers or contactors are poorly rated, single-phase fuse blowing and contact failures may occur frequently. In heavily used fan or pump systems, selecting protective devices properly rated for maximum operational current is crucial.
- Site Vibration and High-Temperature Environments
- Fans and pumps often operate in areas subject to vibration and temperature swings. Loose screws and increased contact resistance are common. Regular inspection schedules and using anti-vibration measures, such as thread-locking compounds on terminal screws, can improve connection reliability.
- Internal Component Damage
- Once external phase-loss causes are ruled out and the fault persists, open the casing to check for damage on the rectifier bridge, DC bus, or sensor board. Any burn marks, bulged capacitors, or cracked circuit traces may indicate the root failure. In such cases, a specialist or authorized service should handle repairs or replacements.
V. Fault Management and Maintenance Steps
- Emergency Measures
- If production needs to resume quickly after verifying balanced three-phase supply, attempt to reset or re-power the drive to see if the alarm disappears. This could indicate only a temporary fault.
- If the fault cannot be cleared, temporarily switch the motor to run at line frequency (assuming the motor and process allow direct-on-line starts) to maintain production. Note that this bypasses the benefits of variable speed control, and starting current may spike significantly.
- Long-Term Solutions
- Following the guidelines in the drive manual (Sections 1-5, 1-6 on input power considerations), add a suitable line reactor or EMI filter to increase the drive’s immunity to supply disturbances.
- If a fuse, breaker, or contactor is mismatched, replace or upgrade it per the drive’s power specifications.
- Conduct regular inspections of both the drive and its upstream components. For demanding fan/pump environments, shorten the service interval accordingly.
- Testing Hardware Components
- If an internal failure is suspected, test the rectifier module or filter capacitors for short, open circuit, or performance degradation. Checking the driver board and DC bus voltage sensors thoroughly is advisable.
- Replace damaged modules or send the drive for professional repair as needed. After repair, test the drive under no-load conditions, ensuring the fault does not recur, then reintroduce the motor load for final verification.
VI. Conclusion
PowerFlex 400 series drives are celebrated for their reliability and versatility, but under harsh or improperly maintained conditions, FAULT 017 (Input Phase Loss) may still occur. Essentially, this fault indicates a missing or unbalanced three-phase input supply. The root cause might be an external breaker or fuse issue, a loose terminal, or damage within the drive’s rectifier or detection circuitry. Operators should first confirm that the external supply is reliable and properly balanced, then troubleshoot and service drive components if necessary. Avoiding a hasty replacement of the drive without investigating the power system’s hidden risks is also key.
For routine maintenance and prevention, pay close attention to line cable connections, proper fuse ratings, and sudden system surges. When justified, install line reactors or EMI filters and maintain inspection logs. Only by thoroughly addressing the underlying causes can you reduce the frequency of FAULT 017, thereby extending the life of the drive and enhancing production efficiency.
In short, FAULT 017 is not merely a problem internal to the drive—it reflects a combined effect of input power and load conditions. Both short-term fixes and long-term measures require checking power supply, protective components, and the drive itself. A full understanding of the alarm’s meaning and trigger logic empowers you to tackle it effectively, ensuring stable operation of your PowerFlex 400 drive in complex industrial environments.