The Milan M5000 series variable frequency drive (VFD) is a high-performance vector control drive, suitable for a wide range of industrial applications. This guide provides detailed information on how to operate and configure the VFD, including parameter initialization, password settings, control mode selections, fault code analysis, and troubleshooting methods.
1. VFD Control Panel Functions
1.1 Basic Functions of the Control Panel
The control panel of the Milan M5000 VFD provides users with various control and configuration options, including:
- Stop/Reset Key: Stops the device or exits the fault state.
- Confirm Key: Confirms the set parameters and makes them active.
- Jog Key: Enables jog mode, allowing the VFD to run at a predefined frequency in small increments.
- Forward/Reverse Key: Controls the forward or reverse direction of the motor, switching its rotation direction.
- Menu Key: Accesses the menu settings for parameter adjustments.
- Analog Potentiometer: Used to adjust the output frequency of the VFD.

1.2 How to Initialize Parameters (Restore Factory Settings)
To restore the factory settings, users can access P3.01 from the menu and select “Restore Factory Defaults”. This operation will clear all customized settings and return the device to its factory default state.
1.3 How to Set and Remove Password
The VFD supports password protection to prevent unauthorized users from modifying critical parameters. To set a password, use function code P9.15:
- Enter P9.15 to set a four-digit password to activate password protection.
- To remove the password, input the correct password and select “Disable Password Protection” in P9.15.
1.4 How to Set Parameter Access Restrictions
Users can configure parameter access restrictions via function code P3.01, allowing them to limit which parameters can be modified by unauthorized users. This can help secure sensitive settings by requiring a password for certain parameters.
1.5 How to Copy Parameters to Another VFD
The P3.02 function allows users to copy the parameters from one VFD to another. By selecting “Upload” and “Download” options, users can transfer settings between devices, making configuration easier for multiple VFDs.
2. Terminal Forward/Reverse Control and External Potentiometer Speed Control
2.1 Terminal Forward/Reverse Control
The Milan M5000 VFD supports forward/reverse control through terminals. Connect the FWD (Forward) and REV (Reverse) terminals properly, and use either the control panel or external terminal input signals to control the motor’s direction.
2.2 External Potentiometer Speed Control
The VFD allows frequency adjustment via an external potentiometer. The potentiometer should be connected to the VCI or CCI terminals. After selecting “External Potentiometer” in P0.01, users can control the VFD’s output frequency by adjusting the potentiometer.
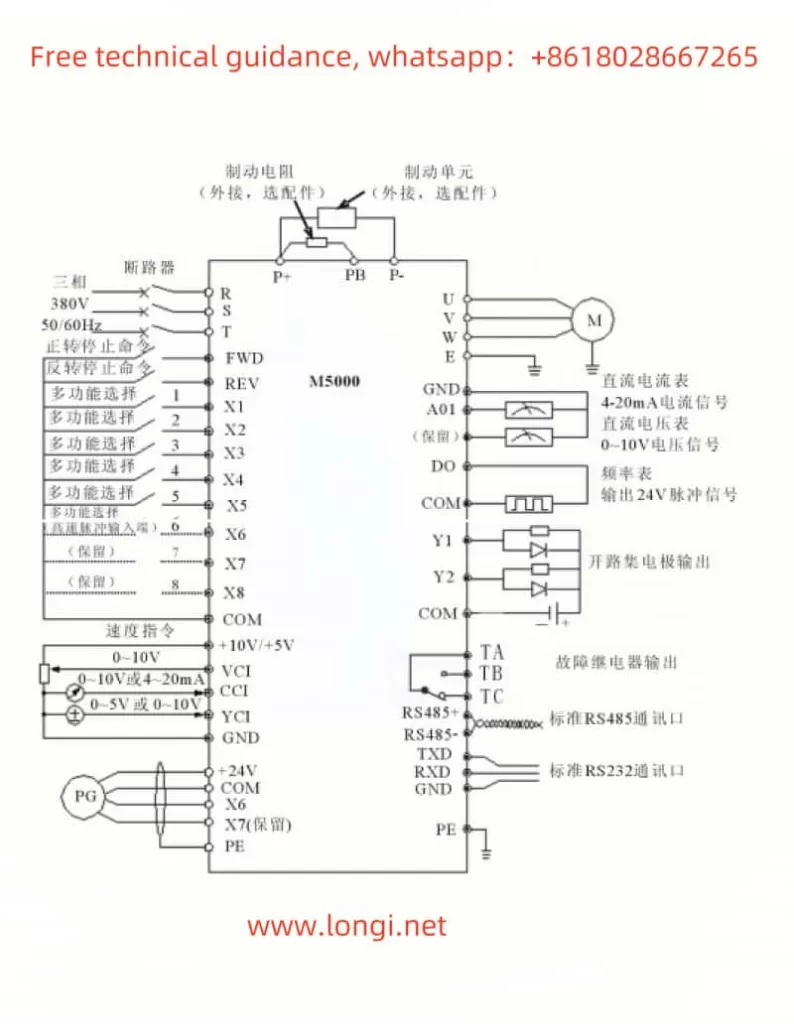
3. Function Code Details
3.1 Frequency Channel Selection (P0.01)
Function code P0.01 allows users to select the frequency setting channel. This defines how the frequency is set (from the control panel, external potentiometer, or analog input). Common options include:
- 0: Keyboard analog potentiometer setting.
- 1: Keyboard digital setting.
- 2: Terminal UP/DOWN frequency setting.
- 4: Serial communication frequency setting.
- 5: Analog VCI input frequency setting.
3.2 Run Command Channel Selection (P0.03)
Function code P0.03 selects the input channel for the run command. This setting allows users to define how the VFD receives start/stop commands. Common configurations include:
- 0: Control panel command.
- 1: Terminal command (e.g., FWD/REV terminals).
- 2: Serial communication command.
- 3: Control terminal command (using X1~X6 multifunction input terminals).
3.3 Starting Frequency Setting (P1.00)
P1.00 is used to set the VFD’s starting frequency. This setting determines the initial frequency at startup. It is typically set to 0.00Hz or a minimum start frequency (e.g., 0.4Hz) to ensure smooth motor startup.
4. Fault Codes and Troubleshooting Methods
4.1 Common Fault Codes
The Milan M5000 VFD is equipped with a variety of fault codes to help users diagnose problems. Common fault codes include:
- E-01: Overcurrent fault, usually caused by an excessive load or motor blockage. Check the motor and load status.
- E-02: Overvoltage fault, often due to high grid voltage or incorrect braking unit settings. Check input voltage and braking system.
- E-03: Undervoltage fault, typically caused by low supply voltage. Ensure the input voltage is correct.
- E-04: Overheating fault, which may be caused by poor ventilation or prolonged high-load operation. Check the cooling system.
- E-05: Overload fault, possibly due to the motor running above its rated capacity. Ensure the motor and load are properly matched.
- E-06: Communication fault, often caused by issues with the RS485 communication wiring or communication protocol settings. Check the wiring and protocol settings.
- E-07: Motor grounding fault. Verify proper motor grounding.
4.2 Fault Troubleshooting Methods
When encountering faults, users should:
- Refer to the fault code table to understand the specific issue.
- Check the power supply, motor, and wiring to ensure everything is functioning correctly.
- Use the fault reset function on the control panel to clear the fault and restart the device.
Conclusion
The Milan M5000 VFD offers flexible configuration and high-efficiency control for various industrial applications. With this guide, users can easily configure parameters, choose control modes, and troubleshoot common faults. Mastering these features will help users optimize device performance and extend its lifespan.
