Exploring the Major Causes of Damage to Inverter Output Modules
In variable speed drive (VSD) systems, damage to the inverter output module is an issue that cannot be ignored. This article delves into several primary reasons behind this failure, analyzing the underlying logic and mechanisms to provide valuable insights for relevant practitioners.
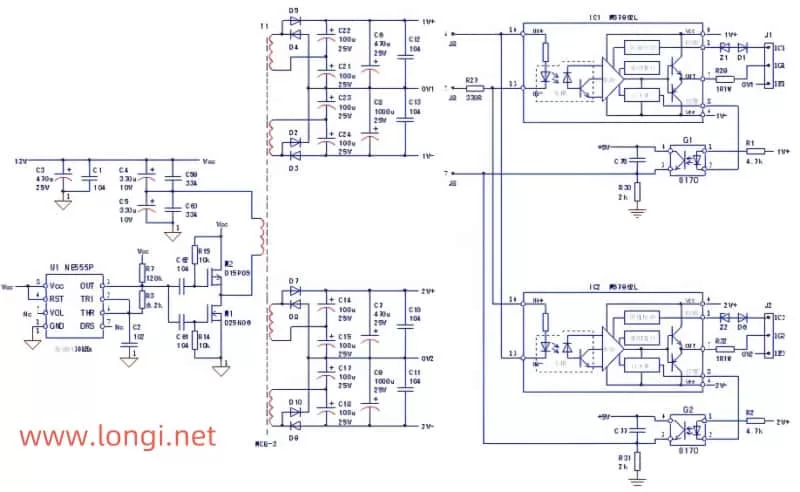
I. Damage Caused by Abnormal Loads
Despite the considerable sophistication of protective circuits in inverters, their protective capabilities may still be limited when faced with abnormal loads. Inverter manufacturers have invested significant effort in protecting inverter modules, employing various measures such as output current detection and IGBT voltage drop detection to achieve the fastest possible overload protection. However, when motors themselves have underlying issues like insulation aging or winding defects, even comprehensive protective functions of the inverter may not fully prevent module damage.
Especially in cases where motors have been operating for many years and their insulation has significantly degraded, connecting them to inverters may result in voltage breakdowns between windings due to high-frequency carrier voltages, leading to short-circuit currents that can instantly subject the inverter module to enormous shocks, causing damage. This type of module damage, triggered by internal motor faults, is difficult for inverter protective circuits to effectively prevent.

II. Damage Caused by Inverter Circuit Issues
- Drive Circuit Failures
The drive circuit is a crucial component of the inverter module, typically supplied by both positive and negative power sources. When the +15V voltage is insufficient or lost, the IGBT cannot be turned on. If the drive circuit’s fault detection function is working properly, the inverter will report an OC signal and shut down for protection. However, if the -5V off-voltage is insufficient or lost, it may cause the IGBT to mistakenly turn on, creating a short circuit that can deal a fatal blow to the module. - Poor Pulse Transmission Path
The PWM inversion pulses output by the CPU pass through a buffer before being sent to the drive IC and then to the trigger terminals of the inverter module. Any interruption in this transmission path can cause the inverter to report an OC fault or operate in an unbalanced phase. Unbalanced phase operation generates DC components and surge currents, which can impact the module and increase the risk of damage. - Failure of Detection Circuits
Current detection circuits and module temperature detection circuits are important barriers for protecting the inverter module. If these circuits fail or malfunction, they will be unable to effectively monitor overcurrent and overheating conditions in the module, thereby losing their protective function. - Decrease in Energy Storage Capacitor Capacity
A decrease in the capacity of the energy storage capacitor in the main DC circuit increases the pulsating components of the DC circuit voltage. During loaded startup, this can cause the inverter module to withstand excessive voltage shocks, leading to damage.
III. Damage Caused by Product Quality Issues
In the market, some domestically produced inverters are criticized for their poor quality and shoddy workmanship. These inverters have obvious deficiencies in the design of protective circuits and the selection of inverter module capacities, making the modules prone to damage. For example, using small-capacity modules, old or defective modules, and ineffective protective circuits significantly increase the risk of module damage.
Conclusion
In summary, the damage to inverter output modules is a result of multiple factors working together. To reduce the risk of module damage, we should approach the issue from multiple angles: strengthen motor maintenance and inspection to ensure motors are in good condition; optimize inverter design to improve the reliability and response speed of protective circuits; and, when choosing inverters, consumers should prioritize product quality and after-sales service to avoid purchasing inferior products. Only in this way can we more effectively protect the safe operation of inverter output modules and extend the lifespan of inverters.
