The ABB ACS580 series inverters are crucial components in industrial automation, renowned for their efficiency and reliability. However, users may encounter various faults during operation, with FAULT 5681 being a particularly common one related to communication issues. This article provides an in-depth analysis of FAULT 5681, specifically addressing the differences between PS communication and PU communication, as well as the impact of parameter 95.04 on this fault, and offers detailed solutions.

Overview of FAULT 5681
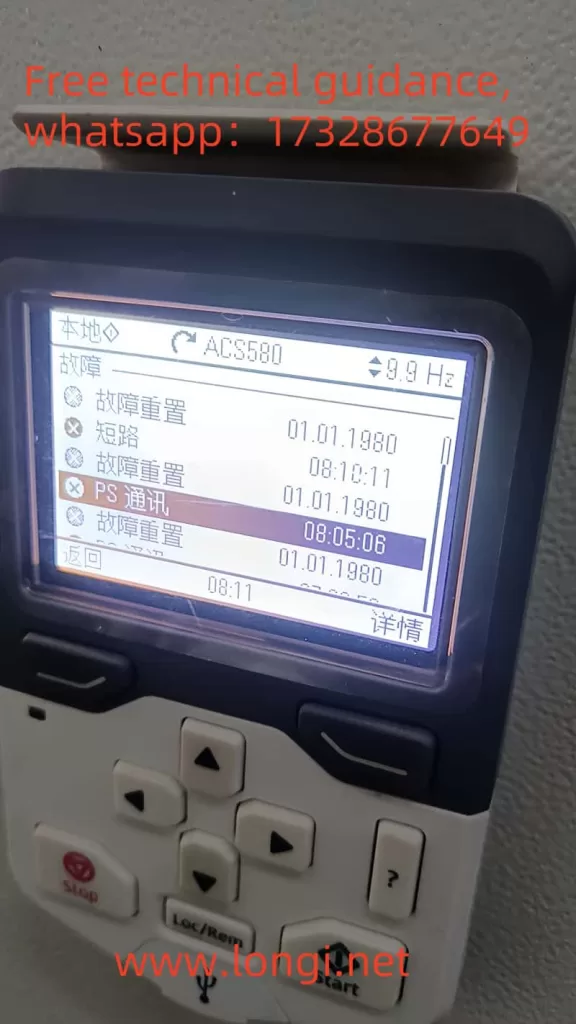
FAULT 5681 indicates a communication error detected between the drive control unit and the power unit, preventing the device from functioning properly. Notably, while the manual may refer to “PU communication issues,” the operator panel might display “PS communication issues,” leading to confusion. In reality, PS communication and PU communication represent two distinct communication protocols and interfaces in ABB inverters.
- PS Communication: Utilizes a serial communication interface (RS485) for point-to-point communication, suitable for smaller systems with its simplicity and directness.
- PU Communication: Based on TCP/IP protocol and Ethernet interface, PU communication caters to larger systems, offering higher flexibility and scalability.

Fault Analysis
- Misunderstanding of Communication Types: Users must clarify that the “PS communication issues” displayed on the operator panel do not equate to “PU communication issues” mentioned in the manual. FAULT 5681 specifically refers to issues within PS communication.
- Control Unit Power Supply: Parameter 95.04 governs the power supply method (internal 24V or external 24V) for the control unit. Instability or incorrect settings can directly affect communication stability, triggering FAULT 5681.
- Communication Line Faults: Improper connections, shorts, or opens in the RS485 communication lines can interrupt communication.
- Power Unit Failure: Damage to the power unit itself may prevent the control unit from detecting its status, leading to communication faults.
Solutions
- Clarify Communication Types:
- Confirm that the fault indeed pertains to PS communication and understand the distinction between PS and PU communication to avoid confusion.
- Inspect and Adjust Control Unit Power Supply:
- Check and confirm parameter 95.04 settings. For external power supply, verify the stability and connection of the external 24V power source. For internal supply, ensure the internal power module functions correctly.
- Adjust or replace the power source if settings are incorrect or power is unstable, and restart the device to test communication recovery.
- Examine Communication Lines:
- Thoroughly inspect the RS485 communication line connections, including interface plugs and line quality, ensuring no shorts, opens, or poor contacts.
- Use a multimeter to test line continuity and replace damaged lines or connectors as needed.
- Verify Power Unit Status:
- Suspect power unit failure? Use professional tools to diagnose its operation.
- Replace or repair the power unit if damaged, coordinating with ABB service for assistance.
- Restart the Device:
- After completing checks and adjustments, restart the device to restore communication. Monitor communication status changes during restart.
- Consult Professional Technical Support:
- If issues persist, contact ABB’s technical support team for detailed troubleshooting and resolution strategies.
Conclusion
FAULT 5681, a prevalent communication issue in ABB ACS580 series inverters, stems from misunderstandings about communication types, control unit power supply issues, faulty communication lines, or power unit malfunctions. By distinguishing between PS and PU communication, inspecting and adjusting control unit power supply, thoroughly checking communication lines, verifying power unit status, timely restarting devices, and seeking professional help when needed, users can effectively resolve this fault. Prompt action ensures uninterrupted production line operations.