“Longi Electromechanical” has more than 20 years of experience in industrial control maintenance, and is one of the earliest companies engaged in VFD repair. Equipped with artificial intelligence AI maintenance instruments, it specializes in emergency repair of various equipment, with high technical efficiency. It has repaired more than 200,000 units of equipment, including ultrasonic, robot, charging pile, inverter,Variable Frequency Drive (VFD), touch screen, servo, intelligent instrument, industrial control machine, PLC and other products. General problems can be repaired on the same day. LONGI promises you that “if it can’t be repaired, we won’t charge you”. And it provides lifelong maintenance service and free technical consultation for inspection! For urgent repair consultation, please call the contact number or add WHATSAPP maintenance hotline: +8618028667265 Mr. Guo;Zalo:+8613922254854
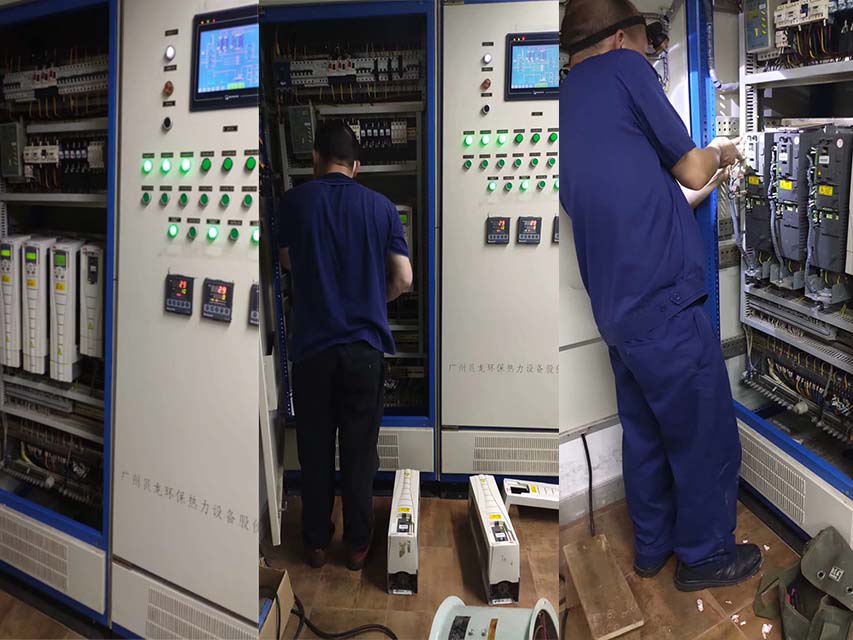

From European and American brands to Japanese, Korean, and Taiwanese ones, until various domestic brands, we have repaired countless models and specifications of VFDs. In the process of serving our customers, we have continuously learned and accumulated maintenance experience to enhance our skills. We specialize not only in repairing VFDs but also in summarizing various maintenance experiences, elevating them to a theoretical level. We have published the book “VFD Maintenance Technology” and offered VFD maintenance training, thereby promoting the development of the VFD maintenance industry. Longi Electromechanical Company has repaired VFDs from the following brands:
European and American Brands
ABB drives, SEW drives, LUST VFD, LENZE VSD, Schneider drives, CT drives, KEB VSD, Siemens drives, Eurotherm VFD, G.E. VFD, VACON VSD, Danfoss VFD, SIEI VFD, AB VFD, Emerson VFD, ROBICON VFD, Ansaldo VFD, Bosch Rexroth VSD, etc.
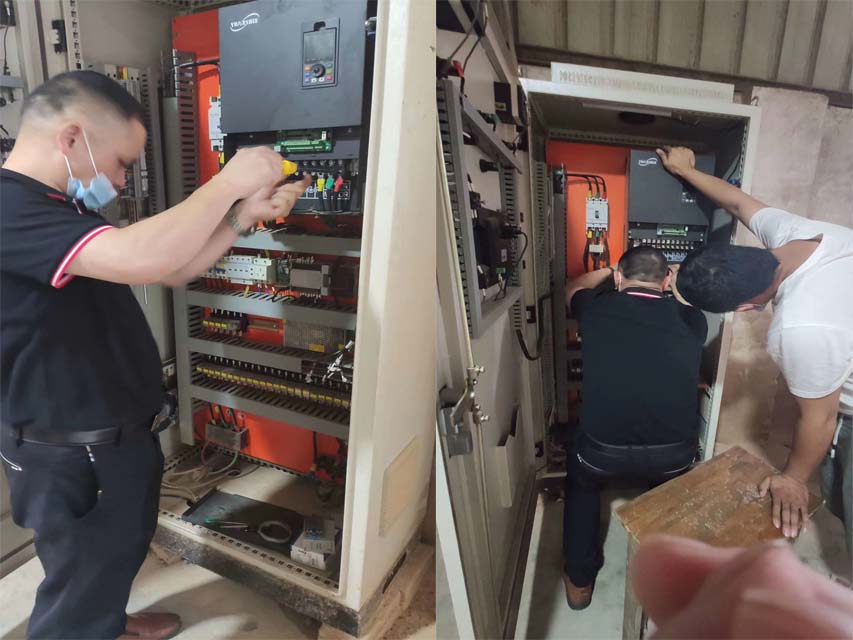

Japanese Brands:
Fuji INVERTER, Mitsubishi INVERTER, Yaskawa INVERTER, Omron INVERTER, Panasonic INVERTER, Toshiba INVERTER, Sumner INVERTER, Tooka INVERTER, Higashikawa INVERTER, Sanken INVERTER, Kasia INVERTER, Toyo INVERTER, Hitachi INVERTER, Meidensha INVERTER, etc.
Taiwanese Brands:
Oulin INVERTER, Delta INVERTER, Taian INVERTER, Teco INVERTER, Powtran INVERTER, Dongling INVERTER, Lijia INVERTER, Ningmao INVERTER, Sanji INVERTER, Hongquan INVERTER, Dongli INVERTER, Kaichi INVERTER, Shenghua INVERTER, Adlee INVERTER, Shihlin INVERTER, Teco INVERTER, Sanchuan INVERTER, Dongweiting INVERTER, Fuhua INVERTER, Taian INVERTER (note: Taian is repeated, possibly a mistake in the original list), Longxing INVERTER, Jiudesongyi INVERTER, Tend INVERTER, Chuangjie INVERTER, etc.
Chinese Mainland brands:
Senlan Inverter, Jialing Inverter, Yineng Inverter, Hailipu Inverter, Haili Inverter, Lebang Inverter, Xinnuo Inverter, Kemron Inverter, Alpha Inverter, Rifeng Inverter, Shidai Inverter, Bost Inverter, Gaobang Inverter, Kaituo Inverter, Sinus Inverter, Sepaxin Inverter, Huifeng Inverter, Saipu Inverter, Weier Inverter, Huawei Inverter, Ansheng Inverter, Anbangxin Inverter, Jiaxin Inverter, Ripu Inverter, Chint Inverter, Delixi Inverter, Sifang Inverter, Geli Te Inverter, Kangwo Inverter, Jina Inverter, Richuan Inverter, Weikeda Inverter, Oura Inverter, Sanjing Inverter, Jintian Inverter, Xilin Inverter, Delixi Inverter, Yingweiteng Inverter, Chunri Inverter, Xinjie, Kemron-Bong Inverter, Nihonye Inverter, Edison Inverter
Other brands:
Migao VFD, Rongqi VFD, Kaiqi VFD, Shiyunjie VFD, Huichuan VFD, Yuzhang VFD, Tianchong VFD, Rongshang Tongda VFD, LG VFD, Hyundai VFD, Daewoo VFD, Samsung VFD, etc.

Longi Electromechanical Company specializes in the maintenance of VFDs and strictly requires its engineers to followlow standard operating procedures. Upon receiving a unit, the engineers carefully inspect its exterior and clarify any fault conditions with the customer before beginning work. Any removed circuit boards are cleaned using ultrasonic cleaning equipment. Repaired circuit boards are coated with high-temperature and high-pressure-resistant insulating paint, dried in a drying machine, and then reinstalled in the VFD, with measures taken to prevent corrosion and interference.
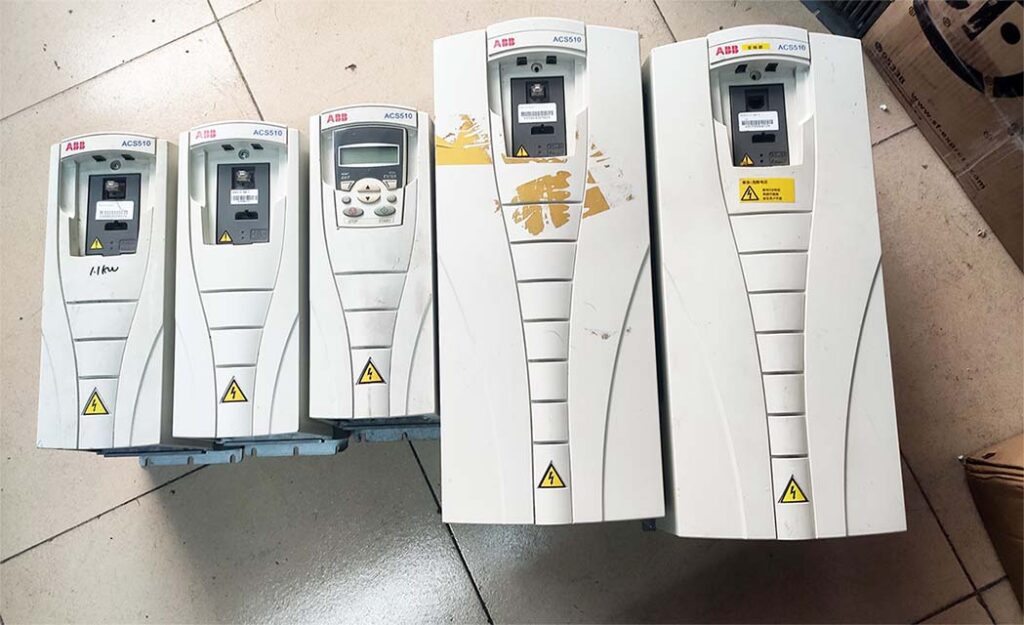

The repaired VFD will undergo a simulated operation with load using a heavy-load test bench to avoid any potential issues that may arise under actual load conditions on site.
When it comes to VFD maintenance, most cases are related to the equipment on site. Sometimes a standalone unit may have been repaired, but it doesn’t work properly when installed on site. In some cases, the problem lies with the system rather than the VFD itself. For such issues, if the customer requests on-site service, we will do our utmost to resolve the problem for them. If the location is far away, such as in another province, we can use tools like video conferencing and phone calls to allow our engineers to remotely diagnose and resolve the on-site issues for the customer.